Well Newborn Care
* Place the infant skin to skin with the mother, once he is stable.
* Assess the Apgar score, at 1 and 5 min after birth.
* Perform a brief physical examination to check that the infant is
healthy (has no major anomalies or birth injuries, his/her tongue &
body appear pink, and has normal breathing).
* Examine the hips to rule out dislocation.
* Umbilical cord care.
► Fix the cord clamp 3-5 cm away from the umbilicus, and cut the
cord using a scalpel.
► Examine for any abnormality (single umbilical artery).
► Wipe the umbilical stump with ethyl alcohol 70%.
* Identification: take footprints and record in the medical record,
and place 2 bracelets with identical hospital numbers (one on the
wrist and the other on the ankle).
Transitional Care (first 4-6 hrs after birth)
* Common signs of disordered transitioning
► Respiratory distress
► Poor perfusion with cyanosis or pallor
► Need for supplemental oxygen
► Hypothermia
* Evaluate every 30-60 min
► Assess HR, RR, axillary temperature, color & tone.
* With suspicion of disordered transitioning
► If stable → observe closely for a period of time.
► If persistent signs → transfer to a higher level of care.
Routine Care
* Keep newborn with mother all the time (rooming-in).
* Perform proper hand washing before handling the newborn.
* Maintain newborn’s temperature
► Encourage skin to skin contact with the mother
► Use hats and proper clothes
* Assess GA using the expanded Ballard Score. Measure and
record the newborn's weight, head circumference, and length,
and then plot against the estimated GA.
* Bathing
► Do not bathe immediately after birth; vernix caseosa does not
need to be removed.
► The first bath can be given with non-medicated soap and
warm tap water once infant's temperature has stabilized (4-6
hrs after delivery).
► Do not bathe the infant in a basin until after the umbilical
stump has fallen off.
* Examine skin for trauma or signs of infection.
* Umbilical cord care
► Keep the cord dry and loosely covered with clean sterile gauze.
► Fold the diaper below the umbilicus.
► If soiled, wash with soap and clean water and dry it well.
► Apply alcohol after each diaper change.
* Place the newborn infant supine (on the back) to sleep and not
prone (on the stomach).
* Routine medications
► Give vitamin K1 (0.5-1 mg IM) within 2 hrs of life.
* Feedings
► Support immediate and exclusive breastfeeding during the
first hr postpartum preferably in the Delivery Room.
► Offer standard term formula to infants for whom breastfeeding
is contraindicated at least every 3-4 hrs.
Instructions to the Mothers or Other Care-Givers
* Observe baby’s temperature, respiration & effort at feeding.
* Observe for passage of urine and stools.
Vaccination
* Educate parents about vaccination schedule.
* Administer HBIG (0.5 ml/kg IM) to all newborns of HBsAg positive
mothers as soon as possible after birth (within 12 hrs),
followed by HBV vaccine (0.5 ml IM).



















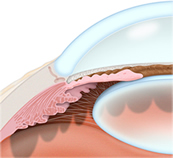 Open-angle glaucoma is the most common type of glaucoma where the fluid in the eye drains too slowly through the network of tiny drainage channels, known as the trabecula. The pressure in the eye increases as the fluid in the eye continues to build. Loss of vision occurs gradually and the vision loss is not always noticed until it becomes irreversible. About 95 percent of glaucoma cases are due to open-angle glaucoma.
Open-angle glaucoma is the most common type of glaucoma where the fluid in the eye drains too slowly through the network of tiny drainage channels, known as the trabecula. The pressure in the eye increases as the fluid in the eye continues to build. Loss of vision occurs gradually and the vision loss is not always noticed until it becomes irreversible. About 95 percent of glaucoma cases are due to open-angle glaucoma.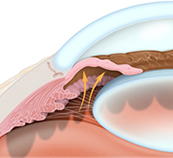 Angle-closure glaucoma occurs when the tiny drainage channels, known as the trabecula, become blocked which then causes a sudden rise in pressure in the eye. This condition is not common but when it occurs it requires immediate medical attention.
Angle-closure glaucoma occurs when the tiny drainage channels, known as the trabecula, become blocked which then causes a sudden rise in pressure in the eye. This condition is not common but when it occurs it requires immediate medical attention.




